PDHPE K–6 Syllabus (2024) – information for school leaders
Learn about the PDHPE K–6 Syllabus (2024) – what has changed and where to get further support.
The Personal Development, Health and Physical Education (PDHPE) K–6 Syllabus (2024) replaces content in the PDHPE K–10 Syllabus (2018). Planning and preparation will commence from 2024 with implementation in 2027.
The syllabus recognises the importance of developing young people’s ability to critically respond to changing health contexts and evolving physical activity options in an increasingly complex, sedentary and rapidly changing world.
Learning in PDHPE equips students with the knowledge and skills to promote and advocate for the health, wellbeing and safety of others in online and offline environments.
Students explore how to build connections and conduct respectful relationships. Health literacy skills are developed, allowing students to critically examine attitudes, behaviours and contextual influences and explore health-related resources.
What you need to know
- In 2025 and 2026, teachers engage with the syllabus, and plan and prepare for implementation of the syllabus.
- Schools are required to enact the new syllabus from 2027.
- There is an expectation that the total time allocated to PDHPE is evenly distributed between Personal Development and Health (PDH) and Physical Education (PE).
- NESA will continue to add teaching advice and support materials to Personal Development, Health and Physical Education (PDHPE) K–6 Syllabus webpages.
The PDHPE K–6 Syllabus (2024) includes:
- explicit teaching of fundamental movement skills, with complementary content to support students with a physical disability, focusing on ability
- explicit teaching of respectful relationships and age-appropriate consent from Early Stage 1
- knowledge and skills to build students’ capacity to be safe in offline and online environments
- broadening students’ knowledge, understanding and skills in personal and community health, physical activity, safety and wellbeing
- explicit content addressing road, water, fire and sun safety, providing multiple opportunities for students to develop and demonstrate their understanding
- content addressing learning in nature and the outdoors and the benefits to health and wellbeing
- the development of self-management and interpersonal skills enabling students to build connections and manage respectful relationships in online and offline environments
- using subject-specific vocabulary to express and communicate students’ understanding of health, safety and wellbeing through Creating Written texts (CWT) which
- focuses on students using vocabulary and language to communicate in Early Stage 1 and Stage 1
- is embedded within PDHPE content in Stage 2
- is an assessable outcome in Stage 3
- making connections through related content in other key learning areas
- removing duplication of dance content, now represented in the Creative Arts K–6 Syllabus
- access content points for students with significant intellectual disability (K–6).
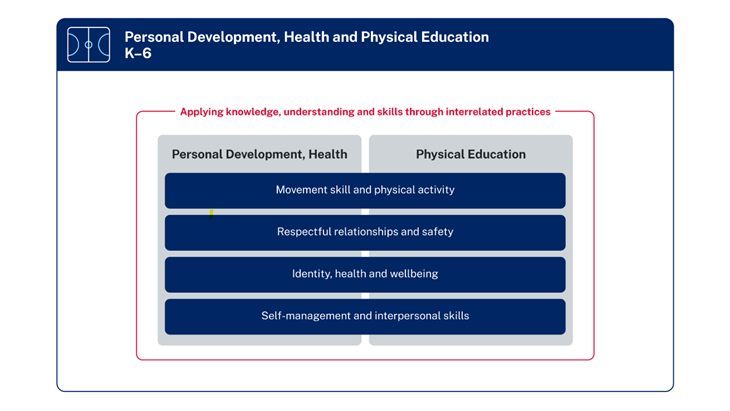
The following diagram shows the organisation of the outcomes and content for the Personal Development, Health and Physical Education (PDHPE) K–6 Syllabus (2024).

Prior to implementing the PDHPE K–6 Syllabus (2024), leaders will need to consider the following:
- The complexities for staff working towards the familiarisation and implementation of four new syllabuses, Creative Arts, HSIE, PDHPE and Science and Technology.
- The department’s Models of curriculum implementation – primary provides suggestions of when these four syllabuses can be enacted which will impact planning, programming, assessment and reporting across the school.
- Supporting teachers’ understanding of
- the evidence base supporting the development of the PDHPE K–6 Syllabus (2024)
- the Controversial Issues in Schools Policy and Procedures, essential to teaching various aspects of the PDHPE K–6 Syllabus (2024).
- Resource and budget implications including
- equipment, facilities and resources for practical application
- time for staff to engage with syllabus features, content and expectations
- professional learning to build staff capacity, including explicit teaching and Curriculum planning K–12 to optimise learning for all students in PDHPE.
The syllabus for PDHPE K–6 (2024) is based on evidence highlighting that:
- physical activity is vitally important for children’s health, wellbeing, development and learning (OECD, 2019)
- the development of essential movement skills competency during childhood lays the foundation for an active lifestyle during adolescence and into adult life (Pill and Harvey, 2019)
- the development of self-management and interpersonal skills support success in learning (Opstoel et al. 2019)
- respectful relationship education works best when it is a school-wide approach with age-appropriate content that supports students in understanding, developing and maintaining respectful relationships (Our Watch, 2021).
The full evidence base can be found in 'Bibliography: PDHPE K–6, NESA, 2024' within NESA's Teaching and learning support.
Personal Development, Health and Physical Education (PDHPE) K–6 Syllabus (2024) © NSW Education Standards Authority (NESA) for and on behalf of the Crown in right of the State of New South Wales, 2024.
- To what extent do staff understand the PDHPE K–6 Syllabus (2024) and the evidence underpinning the new syllabus?
- How will the PDHPE K–6 Syllabus (2024) affect classroom practice? What is in place to support and evaluate this practice?
- What school practices and systems are in place to support teacher professional learning? How are these evaluated to maximise support for teachers?
- What resources are required to commence PDHPE K–6 Syllabus (2024) implementation and meet planning, programming, assessing, and reporting requirements? How is this embedded into the School Excellence Plan (SEP)?
- How will the school’s plan for PDHPE K–6 Syllabus (2024) implementation be evaluated? How might this evaluation inform the implementation of other syllabuses?
- PDHPE K–6 Syllabus (2024) (NESA, 2024)
- Introduction to PDHPE K–6 Syllabus – video (3:47), (NESA, 2024)
- PDHPE K–6 Syllabus – Teaching and learning support (NESA, 2024)
- Planning, programming and assessing PDHPE K–6
- Controversial issues in schools policy and Controversial issues in schools procedures – some aspects of the PDHPE K–6 Syllabus (2024) may be viewed as sensitive or controversial, such as learning about abuse, child protection, drugs, respectful relationships, sexuality education and violence.
- PDHPE communicating with parents and carers – it is essential that principals maintain communication with parents and carers on teaching and learning programs, visiting speakers, external providers and other school activities, including student-organised activities, in which controversial issues may be addressed.
- Guidelines for engaging external providers – use visiting speakers and external providers only where this adds value to existing teaching and learning practice as principals and teachers have primary responsibility for education programs in schools.
- Sport and physical activity policy – plan for 150 minutes of sport and physical activity weekly – ensure sport and physical activity is incorporated into the weekly timetable and that activities are inclusive and adaptive for all students.
- Specific sport and physical activity safety guidelines – supports principals to mitigate risks, as well as offer essential information for planning physically active student activities, including weekly sport, physical education, excursions and recreational activities at school camps.
Further support
- See NSW Department of Education Leading curriculum K–12 for updates and additional information
- Email: pdhpek6@det.nsw.edu.au
- Contact the primary curriculum team: primarycurriculum@det.nsw.edu.au
- Join the Primary Curriculum statewide staffroom (staff only)