Mathematics K–10 Syllabus (2022) for Years K–2 – information for school leaders
The Mathematics K–10 Syllabus (2022) includes outcomes and content for Years K–2.
The NSW Mathematics K–10 (2022) Syllabus recognises the critical importance of early mathematics skills in the early years of school. Through the study of mathematics, students develop essential concepts and skills and apply them to deepen their understanding of the world. In mathematics K–2, students:
- develop essential numeracy skills and mathematical fluency
- identify, describe and apply patterns and relationships
- develop their reasoning and problem-solving skills
- apply their knowledge and understanding in practical situations and make informed decisions.
What you need to know
- Implementation began in some schools in 2022 and the syllabus will be taught in all NSW primary schools from 2023.
- Streamlined content makes clear the essential knowledge, skills, and understandings for mathematics.
- The syllabus recognises the importance of reasoning in strengthening foundational mathematical skills.
- An overarching Working mathematically outcome highlights interrelated processes of reasoning, communicating, problem-solving, fluency and understanding.
- The outcomes have been organised to reflect the connections across and within the mathematics concepts of number and algebra; measurement and space; statistics and probability.
- There is a greater focus on the language used in mathematics to better support learning and understanding.
- National Numeracy Learning Progressions Version 3 are mapped to content
Prior to implementing the Mathematics K–2 Syllabus, leaders will need to consider the following:
- complexities for staff working from 2 syllabuses to teach mathematics – K–2 and 3–6
- There are differences including structure, language, and pedagogy.
- This will impact planning, programming, assessment and reporting across the school.
- targeted support and opportunities for mathematics professional learning to build teacher confidence, particularly with the processes of working mathematically
- resource and budget implications including
- identifying teacher strengths and expertise to support curriculum implementation in your school
- professional learning to build staff capacity
- equipment and materials that may be useful to support learning.
The K–2 content in the Mathematics K–10 Syllabus includes:
- a new structure that highlights foundational numeracy skills
- significant revision to the structure and naming of the sub-strands
- a new aim, rationale, and other introductory components that are informed by evidence
- new outcomes and content that are informed by evidence and identify skills needed by all students to develop competence in mathematics
- a greater emphasis on the development of reasoning for students to support a deep understanding of mathematical concepts
- one overarching outcome for working mathematically that describes the thinking and doing of mathematics
- content groups that assist teachers to identify key knowledge and skills for each focus area
- key progress points that have been developed by NESA
- They provide examples of tasks that teachers may use to investigate student understanding and progress.
- examples that have been separated from the content
- This makes it clearer what is syllabus content and what is provided as support.
- access points for students with significant intellectual disability
- teaching advice to support understanding of the content of the syllabus and to make informed pedagogical decisions.
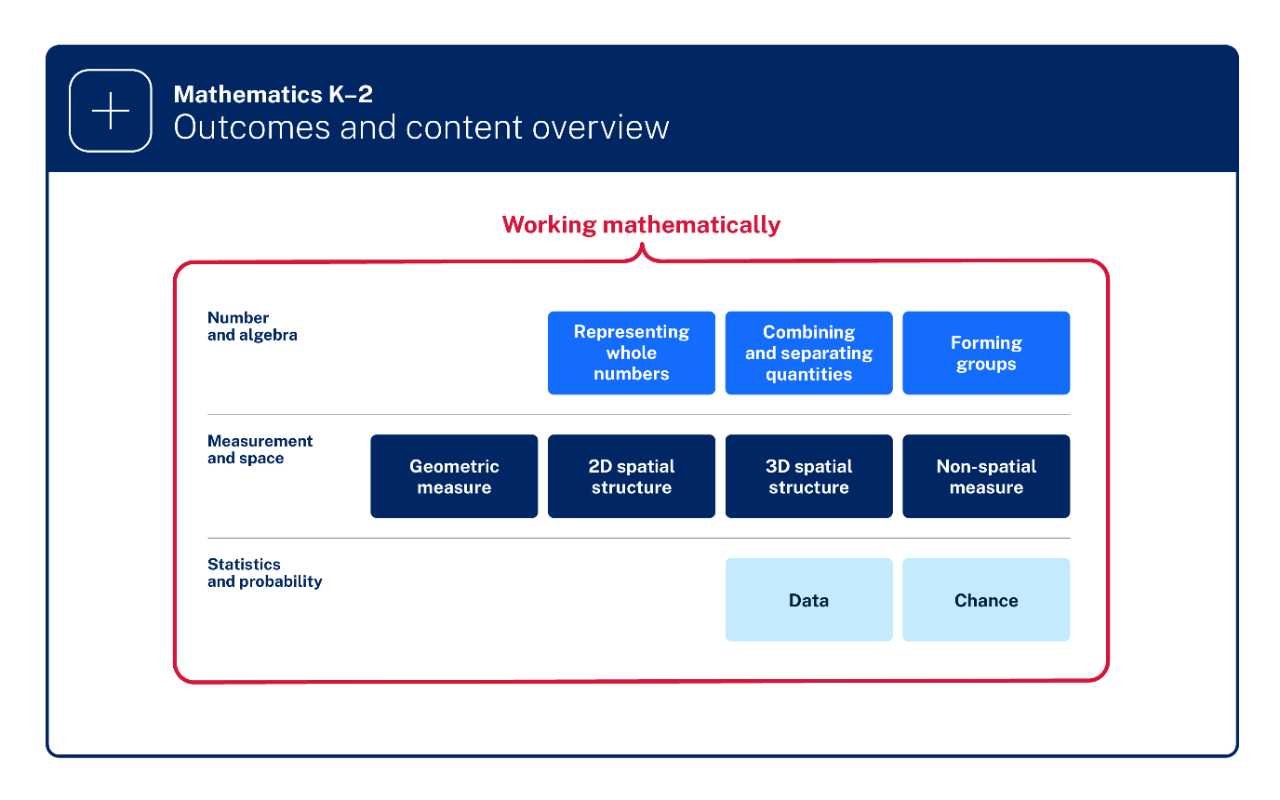

Mathematics outcomes and content overview image is from the Mathematics K–2 Syllabus (2022) © NSW Education Standards Authority (NESA) for and on behalf of the Crown in right of the State of New South Wales, 2024.
The syllabus for mathematics K–2 is based on evidence that highlights the importance of:
- understanding the symbols that represent quantity
- learning the sequence of counting words and making the association between the words and quantities
- learning different ways of representing quantity – objects, words and symbols – as well as understanding that ten (10), for example, is not only a word or symbol but a combination of different number pairs, such as 5 and 5, 4 and 6, or 3 and 7
- knowing how to use 10 and 100 as units
- identifying links between measurement, space and number
- understanding how structures are organised and related
- being able to provide the reasoning behind the solution to a problem.
Professional learning for the teaching and learning of mathematics:
- Mathematics K–10 Syllabus (2022) – including teaching advice
- Introduction to the Mathematics K–2 Syllabus (video 2:41)
- Thinking mathematically K–6 resources
- Curriculum Reform Communities
- NSW Curriculum Reform webpage for updates and additional information.
Further support
- See the department's curriculum reform webpage for updates and additional information.
- Mathematics curriculum team
- Planning, programming and assessing mathematics K–6
- Email mathematicsk6@det.nsw.edu.au
- Email Primarycurriculum@det.nsw.edu.au
- Primary curriculum statewide staffroom (staff only)